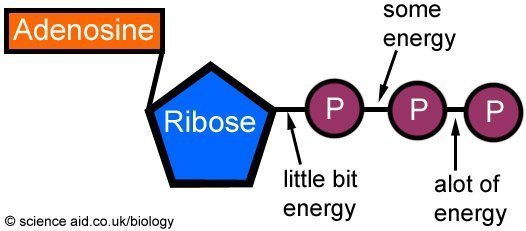
42 label the 3 parts of the atp molecule
Identify the three components [(i),(ii) and (iii)] of ATP molecule ... (i)- Ribose ; (ii)- Triphosphate group ; (iii)- Guanine Answer Correct option is A (i)- Ribose; (ii)-Triphosphate group ; (iii)- Adenine ATP or adenosine triphosphate or Adenine- ribose-phosphate-phosphate-phosphate. The bonds joining the additional phosphate groups o the nucleotides are called high energy or energy-rich bonds. Actin and Actin-Binding Proteins - PMC Structures of the actin molecule and actin filament. (A) Ribbon diagram of the actin molecule with space-filling ATP (protein data bank [PDB]: 1ATN). N, amino terminus; C, carboxyl terminus. Numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 label the four subdomains. (B) Space-filling model of actin showing the nucleotide-binding cleft with ATP in situ and barbed-end groove.
Adenosine Triphosphate - ATP - Bristol The 1997 Nobel prize for Chemistry has been awarded to 3 biochemists for the study of the important biological molecule, adenosine triphosphate. This makes it a fitting molecule with which to begin the 1998 collection of Molecule's of the Month. Other versions of this page are: a Chime version and a JMol version. ATP - Nature's Energy Store
Label the 3 parts of the atp molecule
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine ), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate . Contents 1 Structure 1.1 Binding of metal cations to ATP 2 Chemical properties 3 Reactive aspects 4 Production from AMP and ADP ATP synthesis and storage - PMC 12.04.2012 · ATP is universally seen as the energy exchange factor that connects anabolism and catabolism but also fuels processes such as motile contraction, phosphorylations, and active transport. It is also a signalling molecule in the purinergic signalling mechanisms. In this review, we will discuss all the main mechanisms of ATP production linked to ... Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Answer: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.
Label the 3 parts of the atp molecule. Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) 7. From left to right- Adenine - Ribose - Phosphate groups 8. The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) … View the full answer DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). R2R9T_ATPCellEnergy (1).docx - Biology ATP Cell Energy... Biology ATP Cell Energy Directions: Answer the following questions. 1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP molecule. Use the molecule from the lesson material or find one on your own (cite the source please). Using the diagram, label the 3 parts that make up an ATP molecule. 2. Explain (or use diagrams to illustrate) how energy is released from ATP molecules. ... mechanisms that can turn off or reduce an enzyme are ... Jun 09, 2022 · oxidation when a phosphate is removed from a molecule 2. phosphorylation a chemical reaction in which oxygen is combined with another substance 3. dephosphorylation when a phosphate is added to a molecule Question #10MultipleChoice Score: All of the chemical reactions in an organism for maintenance of life processes are called ...
Biology ATP Flashcards | Quizlet What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? 1. Adenine 2. Phosphate Groups 3. Ribose. Write the reaction for the breakdown of ATP. ... 1/2 molecule oxygen gas, two hydrogen ions, and 2 electrons oxygen - released 2Hions - make NADPH 2e - replace those lost to electron transport chain. What is the Structural Difference Between ATP and ADP ATP molecule is composed of a ribose, an adenosine, and three phosphate groups. The first phosphate molecule is referred to as the alpha phosphate group. The second is the beta while the third is the gamma phosphate group. The three phosphate molecules are linked through negatively-charged oxygen molecules. adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ... quizlet.com › 467858933 › photosynthesis-flash-cardsPhotosynthesis Flashcards | Quizlet The electron from a molecule of water goes with H+ to the ATP Synthase, to which it joins the sugar G3P. Describe how ATP is produced in the light reactions. A electron goes through PSII then goes to the cytochrome complex then to PSI to which it goes to the ATP synthase.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Structure of ATP This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source Answered: Part 1: The structure of ATP TP… | bartleby Part 1: The structure of ATP TP consists of 3 parts: I adenine molecule, I ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. nergy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. 1. COLOR the following ATP molecules below and provide a key to show the 3 parts. 2. Label the area that represents the HIGH ENERGY bond. › pmc › articlesATP synthesis and storage - PMC Apr 12, 2012 · Similar ATP release could be induced also in astrocytes and glial cells of the retina . The ATP concentration within these stores appears significantly different, dependent on the cell type, but it can reach high levels of around 150–200 mM . Also, other nucleotides were found to be co-compartmentalized, especially GTP, UTP, and ADP ... ATP/ADP | Photosynthesis Quiz - Quizizz Which structures shown in the Figure make up the ATP molecule? ATP/ADP DRAFT. 9th - 10th grade. 1705 times. Biology. 65% average accuracy. 2 years ago. adamsb. 3. Save. Edit. Edit. ATP/ADP DRAFT. 2 years ago ... Using the figure, which parts of the molecule must the bonds be broken to form an ADP molecule? answer choices . A and B. B and C. C ...
atp molecule labeled - DaVinci Custom Linear Fireplaces Label each part of the atp molecule above in the spaces provided. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. How does atp differ from adp. Chemical bonds in phosphate groups what are the three parts of an atp molecule. n. Combined with microchannel flow cells and microfluidic control, allow individual fluorescently labeled protein and DNA ...
What are 3 parts of an ATP molecule? - AskingLot.com The three components of an ATP moleculer are a 5 carbon sugar - ribose, Adenine a base found in DNA and a chain of three phosphate groups attached to the ribose backbone. The function of ATP is to store energy in small usable units. Describe how ATP stores energy. Also, what are 3 ways the cell uses ATP? ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
1. Label the parts of the ATP molecule using the word bank. Label the parts of the ATP molecule using the word bank. Word Bank: Ribose. Phosphate Group. Adenine. 1. How is energy released from ATP?5 pages
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Magnesium_in_biologyMagnesium in biology - Wikipedia For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
Photosynthesis Flashcards | Quizlet The vascular bundle is used to transport organic molecules from the leaf to other parts of the plant. Why are leaves green? It is because of chloroplasts, the organelle where photosynthesis. On diagram 5, fill in the labels with the following descriptions to show the connections between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. Left side, Top to bottom: ATP, NADPH, O2, Right side, top …
What are the three parts of the ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
SKELETAL MUSCLE ORGANIZATION - CAS It is the ATP that provides the energy for muscle contraction. Each of the myosin heads is associated with two myosin light chains that play a role in regulating the actions of the myosin heads, but the exact mechanism is not fully understood. The three dimensional arrangement of the myosin heads is very important. Imagine that you were looking at a thick filament from the …
› uploads › coursesenergy and training module - World Triathlon A molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the “energy currency” of the body. ATP powers most cellular processes that require energy including muscle contraction required for sport performance. Where does ATP come from and how is it used? ATP is produced by the breakdown of fuel molecules—carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems.Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg 2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active.





Post a Comment for "42 label the 3 parts of the atp molecule"